Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Key Differences Explained (2026 Guide)

📋 En bref (TL;DR)
- Bitcoin (BTC): First cryptocurrency, created in 2009, designed as a store of value with a capped supply of 21 million BTC
- Ethereum (ETH): Programmable blockchain launched in 2015, enables smart contracts, DeFi, and NFTs
- Consensus: Bitcoin uses Proof of Work (mining), Ethereum uses Proof of Stake since 2022 (99.95% less energy)
- Speed: Bitcoin ~7 tx/sec (+ Lightning Network), Ethereum ~30 tx/sec (+ Layer 2 like Arbitrum, Optimism)
- Supply: Bitcoin = 21 million max (scarce), Ethereum = unlimited but deflationary since EIP-1559
- Investment: Bitcoin = more stable and institutional, Ethereum = higher potential (and risk)
- Complementary: Both serve different needs — many investors hold both (60-70% BTC, 20-30% ETH)
“Bitcoin or Ethereum?” — This is THE question every crypto beginner asks. Together, these two giants represent over 65% of the crypto market, but they are fundamentally different in their design, purpose, and use cases.
Bitcoin is often compared to digital gold — a scarce asset designed to store value. Ethereum is more like a decentralized world computer — a platform on which thousands of applications are built. Understanding this fundamental distinction will help you make better investment decisions.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll analyze the differences between Bitcoin and Ethereum in detail: their history, technology, use cases, and most importantly, how to choose which one to invest in based on your profile.

What Is Bitcoin? Digital Gold Explained
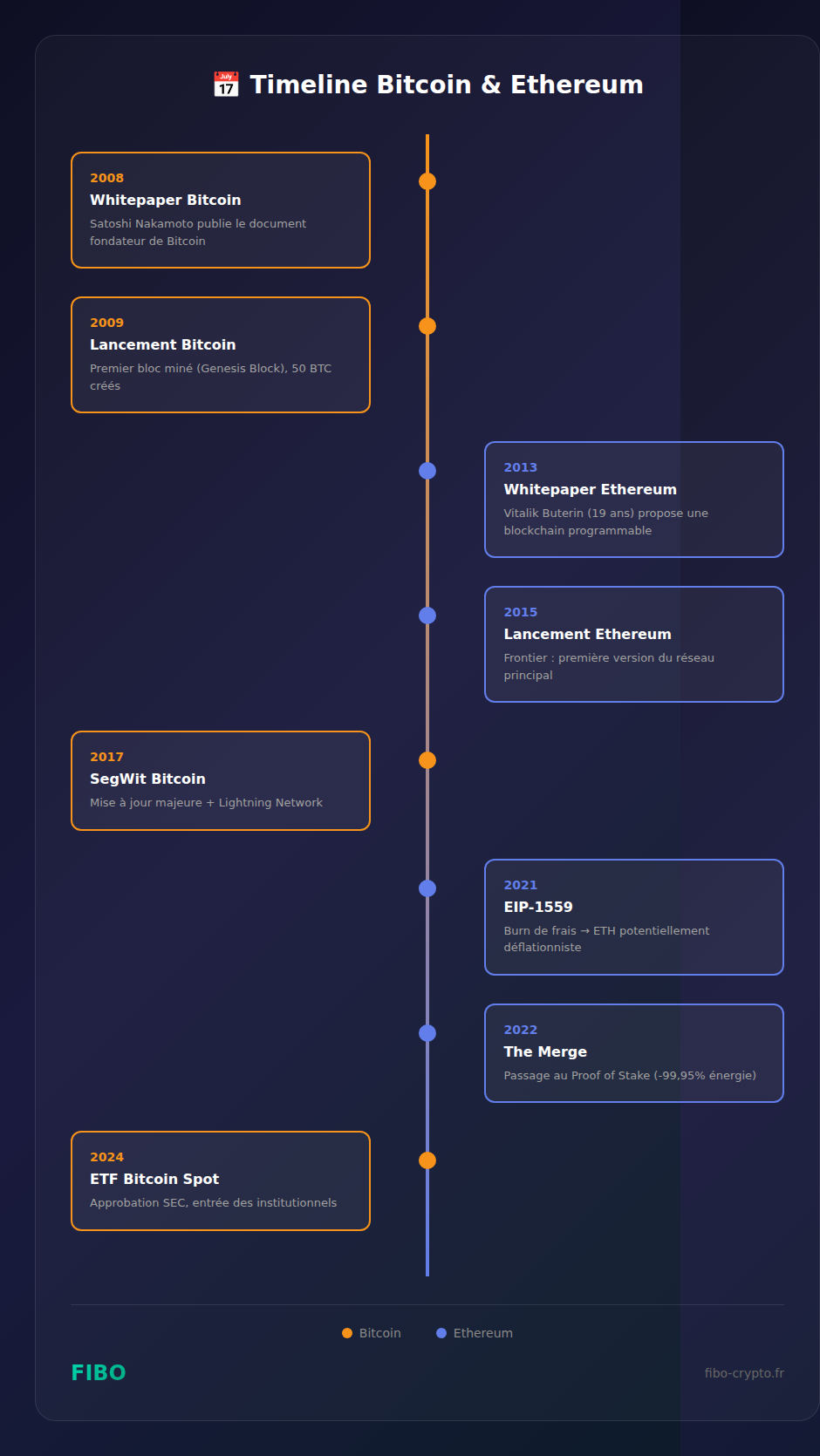
Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency, created in 2009 by the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto. Its goal was revolutionary: to create a decentralized digital currency without banks or governments controlling it.
The Bitcoin whitepaper, published on October 31, 2008, describes a “peer-to-peer electronic cash system.” But over time, Bitcoin has evolved toward a different role: that of a store of value.
Key Characteristics of Bitcoin
- Supply capped at 21 million: this programmed scarcity is written in the code and will never change
- Proof of Work: miners use computing power to secure the network
- Halving every 4 years: mining rewards are cut in half, reducing inflation
- Intentional simplicity: Bitcoin does one thing (transfer value) and does it very well
- Maximum decentralization: over 15,000 nodes distributed worldwide
What Is Ethereum? The World Computer
Ethereum arrived 6 years after Bitcoin, created by Vitalik Buterin when he was just 21 years old. His idea: what if we could program the blockchain?
Where Bitcoin is a calculator (it does one thing very well), Ethereum is a computer. It allows executing programs called smart contracts — contracts that automatically execute when certain conditions are met.
Key Characteristics of Ethereum
- Smart contracts: autonomous programs that execute according to predefined rules
- Proof of Stake: since “The Merge” in 2022, validators stake their ETH to secure the network
- EIP-1559: a portion of transaction fees is “burned,” making ETH potentially deflationary
- Rich ecosystem: DeFi, NFTs, DAOs, and thousands of dApps
- Constant evolution: ambitious roadmap with sharding and ongoing improvements
Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Technical Differences
Understanding the technical differences between Bitcoin and Ethereum is essential for grasping why these two cryptocurrencies serve different purposes.
1. Consensus Mechanism: PoW vs PoS
This is the most fundamental difference since 2022.
Bitcoin uses Proof of Work: miners worldwide use specialized computers (ASICs) to solve complex calculations. The first to find the solution validates the block and receives the reward (currently 3.125 BTC). This system is extremely secure but energy-intensive.
Ethereum uses Proof of Stake since “The Merge” in September 2022. Instead of miners, validators “stake” (put up as collateral) at least 32 ETH. They are randomly selected to validate blocks. This system consumes 99.95% less energy than PoW.
2. Supply and Monetary Policy
Bitcoin has a supply strictly limited to 21 million units. This limit is written in the source code and will never change. About 19.6 million BTC are already in circulation. The last Bitcoin will be mined around 2140. This absolute scarcity is Bitcoin’s main argument as “digital gold.”
Ethereum has no fixed limit, but since EIP-1559’s implementation in August 2021, a portion of transaction fees (the “base fees”) is permanently destroyed. When network activity is high, more ETH is burned than created — making ETH deflationary. Currently, about 120 million ETH are in circulation.
3. Speed and Scalability
Bitcoin can process about 7 transactions per second on its main layer. It’s slow, but it’s a deliberate choice: security and decentralization take priority over speed. For fast payments, the Lightning Network (Layer 2) enables millions of instant, nearly free transactions.
Ethereum handles about 30 transactions per second on its main layer. But with Layer 2 solutions like Arbitrum, Optimism, and Base, the network can reach thousands of tx/sec at lower cost. Planned “sharding” in the roadmap will further increase this capacity.
4. Programmability and Flexibility
Bitcoin is intentionally simple. Its scripting language is limited to prevent security vulnerabilities. Innovations like Taproot (2021) have improved capabilities, and projects like BitVM explore smart contracts on Bitcoin, but that’s not its main purpose.
Ethereum is Turing-complete: you can program any logic on it via Solidity or Vyper. This is what enables complex decentralized applications (Uniswap, Aave, OpenSea), but it’s also what creates risks (bugs and exploits in smart contracts).
Bitcoin Use Cases: Store of Value and Payments
Bitcoin excels in one specific role: storing and transferring value in a decentralized manner.
Bitcoin as “Digital Gold”
- Store of value: protection against inflation and monetary devaluation
- Safe haven asset: in unstable countries (Argentina, Venezuela, Turkey), Bitcoin protects against hyperinflation
- Corporate treasury: MicroStrategy holds over 200,000 BTC; Tesla and Square also own some
- Institutional adoption: Bitcoin Spot ETFs approved in January 2024 attracted billions of dollars
Bitcoin for Payments
- International transfers: sending value without banking intermediaries, 24/7
- Lightning Network: instant and nearly free payments for everyday purchases
- Circular economy: in some communities, Bitcoin is used as everyday currency
Bitcoin is like gold: you buy it, you hold it, you hope it gains value. It’s a passive asset.
Ethereum Use Cases: DeFi, NFTs, and Web3
Ethereum is a platform on which thousands of applications are built. Its value comes from its ecosystem.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
- Decentralized exchanges: Uniswap, Curve, SushiSwap — trade without intermediaries
- Lending and borrowing: Aave, Compound — deposit your crypto and earn interest, or borrow against collateral
- Yield farming: optimize your returns by providing liquidity
- Stablecoins: USDC, DAI, and most stablecoins run on Ethereum
NFTs and Gaming
- Digital art: works sold for millions of dollars
- Collectibles: CryptoPunks, Bored Apes, and thousands of collections
- Blockchain gaming: in-game items truly owned by players
DAOs and Governance
- Decentralized organizations: companies managed by code and community votes
- Collective treasuries: millions managed by smart contracts
Real-World Asset Tokenization
- Real estate: fractional ownership of buildings
- Stocks and bonds: financial securities on blockchain
- Commodities: tokenized gold, oil
Ethereum is like an operating system (Windows, iOS): its value comes from the applications running on it. It’s a productive asset.

Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Which Investment to Choose?
This is THE question everyone asks. Here’s an honest analysis based on different investor profiles.
Choose Bitcoin if…
- You want the least risky option in the crypto universe
- You have a very long-term horizon (10+ years)
- You’re looking for inflation protection
- You prefer simplicity: buy and hold (“HODL”)
- You want to follow institutions (ETFs, corporate treasuries)
- You value maximum decentralization and censorship resistance
Choose Ethereum if…
- You believe in the potential of DeFi and Web3
- You’re willing to accept more volatility for more potential
- You want to use the blockchain (not just own it)
- You’re comfortable with technology and its evolution
- You’re looking for yield through staking (~4% per year)
- You want to invest in the Web3 infrastructure
The Balanced Strategy: Both
The wisest answer is often: hold both. Many experienced investors recommend an allocation like:
- 60-70% in Bitcoin: the stable foundation, “digital gold”
- 20-30% in Ethereum: exposure to the innovative ecosystem
- 0-10% in altcoins: for the more adventurous
This allocation exposes you to the two dominant crypto narratives while limiting overall risk.
Historical Performance: BTC vs ETH
Let’s look at the numbers (while remembering that past performance does not guarantee future results).
Bitcoin
- ATH (All-Time High): ~$126,000 (October 2025)
- 5-year performance: approximately +900%
- Worst drawdown: -83% (2022 bear market)
- Volatility: high but decreasing with institutionalization
Ethereum
- ATH: ~$4,950 (August 2025)
- 5-year performance: approximately +1,500%
- Worst drawdown: -94% (2018-2019 bear market)
- Volatility: higher than Bitcoin
Historically, Ethereum has outperformed Bitcoin during bull markets, but has also suffered more brutal corrections. This reflects the classic risk/reward principle.
Summary Table: Bitcoin vs Ethereum
| Characteristic | Bitcoin | Ethereum |
|---|---|---|
| Created in | 2009 | 2015 |
| Creator | Satoshi Nakamoto | Vitalik Buterin |
| Symbol | BTC | ETH |
| Nickname | “Digital Gold” | “World Computer” |
| Max supply | 21 million (fixed) | Unlimited (deflationary) |
| Consensus | Proof of Work | Proof of Stake |
| Speed | ~7 tx/sec (+ Lightning) | ~30 tx/sec (+ L2) |
| Smart contracts | Limited | Turing-complete |
| Primary use | Store of value | Application platform |
| Staking | No (mining) | Yes (~4% yield) |
| Energy | ~150 TWh/year | ~0.01 TWh/year |
| Market cap | ~$2.5 trillion | ~$600 billion |
| Volatility | High | Very high |
| Ecosystem | Minimalist | Very rich (DeFi, NFTs, DAOs) |
Conclusion: Bitcoin and Ethereum Are Complementary
Bitcoin and Ethereum are not really competing. They address fundamentally different needs:
- Bitcoin answers the question: “How can I store value outside the traditional system?”
- Ethereum answers the question: “How can I create decentralized financial applications?”
That’s why most experienced investors hold both. Bitcoin for relative stability and long-term store of value. Ethereum for exposure to innovation and the growing Web3 ecosystem.
Most importantly, invest only what you can afford to lose, understand what you’re buying, and think long term. Cryptocurrencies are volatile — that’s normal. What matters is your conviction in the technology and your investment horizon.
📚 Glossary
- Bitcoin : First cryptocurrency created in 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto, designed as a decentralized store of value with a supply limited to 21 million units.
- Ethereum : Programmable blockchain launched in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin, enabling the execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
- Blockchain : Distributed and immutable ledger where all transactions are recorded chronologically and verifiably.
- Smart contract : Autonomous program deployed on a blockchain that executes automatically according to predefined conditions, without intermediaries.
- DeFi : Decentralized Finance, a set of financial services (lending, exchanges, savings) operating on blockchain without banks.
- NFT : Non-Fungible Token, a unique digital asset representing ownership of an item (art, collectible, etc.) on the blockchain.
- DAO : Decentralized Autonomous Organization, an entity managed by smart contracts and token holder votes, without central management.
- Proof of Work : Consensus mechanism where miners use computing power to validate transactions and secure the network.
- Proof of Stake : Consensus mechanism where validators stake their tokens to participate in network validation.
- Layer 2 : Scalability solution built on top of a main blockchain to increase speed and reduce transaction costs.
- Stablecoin : Cryptocurrency whose value is pegged to a fiat currency (dollar, euro), like USDC or DAI.
- Staking : Locking tokens to participate in Proof of Stake network validation and receive rewards.
- Halving : Bitcoin event every ~4 years where mining rewards are cut in half, reducing new BTC issuance.
- The Merge : Major Ethereum upgrade in September 2022, transitioning from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake.
- Lightning Network : Bitcoin Layer 2 solution enabling instant, nearly free payments off the main blockchain.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bitcoin or Ethereum: Which is the better investment in 2025?
It depends on your investor profile. Bitcoin is considered less risky and more established — ideal for conservative investors seeking a store of value. Ethereum offers more growth potential but with more volatility — perfect for those who believe in Web3 and want exposure to the DeFi/NFT ecosystem. The most common strategy is to hold both: 60-70% in Bitcoin for stability, 20-30% in Ethereum for growth potential.
Can Ethereum surpass Bitcoin in market cap (the flippening)?
The “flippening” — the moment when Ethereum would surpass Bitcoin in market cap — is theoretically possible but has never happened. In 2025, Bitcoin represents about 50% of the crypto market, Ethereum about 15-20%. The two cryptocurrencies have fundamentally different roles: Bitcoin as a store of value, Ethereum as application infrastructure. A flip would require a major shift in market perception.
Why is Ethereum's price lower than Bitcoin's?
Unit price means nothing by itself! What matters is total market capitalization (price × number of units). Bitcoin has a maximum of 21 million units, Ethereum has about 120 million. Comparing unit prices is like comparing Apple’s share price to Amazon’s — it doesn’t make sense. It’s the market cap and growth potential that matter for investment.
Can I use my Bitcoin in Ethereum's DeFi?
Not directly, since Bitcoin and Ethereum are separate blockchains. But you can use Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) — Bitcoin tokenized on Ethereum. You keep exposure to Bitcoin’s price while accessing Ethereum’s DeFi ecosystem (lending, farming, etc.). Note: this involves trusting the custodians who hold the real BTC.
Which is more secure, Bitcoin or Ethereum?
Both main blockchains are extremely secure and have never been directly hacked. Bitcoin is often considered slightly safer due to its simplicity and battle-tested Proof of Work since 2009. Risks on Ethereum mainly come from poorly coded smart contracts (bugs, exploits) — not the blockchain itself. For simple value storage, Bitcoin has the advantage of simplicity.
Do I need to understand the technology to invest in Bitcoin or Ethereum?
Not in technical detail, but you should understand the basics: why Bitcoin has value (scarcity, decentralization), what Ethereum does (smart contracts, DeFi). This understanding will help you make better decisions and especially not panic during -30% or -50% corrections. Investors who understand what they’re buying are more likely to hold long-term.
How do I buy Bitcoin and Ethereum?
You can buy BTC and ETH on regulated platforms like Binance, Kraken, Coinbase, or Gemini. The process: create an account, verify your identity (KYC), deposit fiat currency via bank transfer or credit card, then buy. For security, transfer your crypto to a personal wallet (hardware wallet like Ledger) rather than leaving them on the exchange.
What's the difference between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake?
Proof of Work (Bitcoin) uses miners who consume electricity to solve calculations and secure the network. It’s very secure but energy-intensive (~150 TWh/year). Proof of Stake (Ethereum) uses validators who “stake” their tokens as collateral. It’s 99.95% less energy-intensive and allows ETH holders to earn rewards (~4%/year). Both mechanisms have their advantages and trade-offs.
📰 Sources
This article is based on the following sources:
- Bitcoin Whitepaper
- Ethereum Whitepaper
- Ethereum.org – The Merge
- CoinMarketCap
- Messari Research
- Glassnode
- Bitcoin Magazine
- The Block Research
Comment citer cet article : Fibo Crypto. (2026). Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Key Differences Explained (2026 Guide). Consulté le 11 February 2026 sur https://fibo-crypto.fr/en/blog/bitcoin-vs-ethereum-differences






