Ethereum Gas Fees Explained: Complete Guide to Transaction Costs (2026)

📋 En bref (TL;DR)
- Gas = blockchain fuel: Unit measuring the computational cost of operations on Ethereum and EVM blockchains
- EIP-1559 formula: Fees = gas used × (base fee + priority fee) — base fee is burned, tip goes to validators
- Variable costs: $2 for a simple ETH transfer, up to $50+ for complex DeFi swaps during congestion
- Layer 2 = massive savings: Arbitrum, Optimism, Base reduce fees by 90-99% while maintaining Ethereum security
- Strategic timing: Weekends and nights (midnight-6am UTC) offer the lowest fees, avoid Tuesday-Thursday 2pm-6pm UTC
- Deflationary: Since August 2021, over 4 million ETH have been burned through transaction fees
- Promising future: Proto-Danksharding and account abstraction are transforming the user experience
Ethereum gas is the fuel powering all your crypto transactions — understanding how it works can save you hundreds of dollars per year. Whether you’re sending ETH, interacting with DeFi protocols, or minting NFTs, every operation consumes gas. This comprehensive guide explains everything: how fees are calculated, tips to pay less, and upcoming changes in 2026.

What is Ethereum Gas? Simple Definition
Gas is a unit of measurement for the computational cost required to execute operations on Ethereum. Think of it like gasoline for your car: the longer and more complex your journey, the more fuel you consume. On Ethereum, the more sophisticated your transaction, the more gas it requires.
This concept was introduced by Vitalik Buterin when Ethereum launched in 2015 to solve two critical problems:
- Spam protection: Without a cost per operation, attackers could flood the network with millions of free transactions
- Fair compensation: Validators securing the network must be compensated for their computational work
The term “gas” refers to the analogy with automobile fuel — every operation has a “fuel cost” you must pay for it to be processed. Unlike real gasoline, gas isn’t a separate cryptocurrency: fees are paid in ETH (or more precisely in gwei, a sub-unit of ETH).
🔑 Fundamental Characteristics of Gas
- Computational unit: Measures the resources (CPU, memory, storage) needed for each operation
- Dynamic pricing: Fluctuates in real-time based on network congestion, like a supply and demand market
- Paid by the sender: You pay the fees, not the recipient of your transaction
- Programmable limit: You define a maximum gas limit to protect your wallet
- Anti-loop mechanism: Automatically stops poorly coded smart contracts that would run infinitely
Why Does Gas Exist? Utility and Network Security
The gas system is the backbone of Ethereum’s economic security — without it, the network would be vulnerable to trivial attacks. Here’s why this mechanism is indispensable:
🛡️ Attack Protection
On a decentralized network like Ethereum, anyone can submit transactions. Without gas fees:
- An attacker could send millions of micro-transactions to saturate the network
- Infinite loops in smart contracts would freeze all nodes
- The network would become unusable because it would be overwhelmed with spam
Gas costs make these attacks economically unviable: spamming the network would cost fortunes in ETH.
⚖️ Efficient Resource Allocation
Ethereum processes approximately 15-30 transactions per second — a limited capacity. Gas creates a natural market where:
- Urgent transactions can pay more to get priority
- Non-urgent operations can wait for off-peak hours
- Resources are allocated to those who need them most
💰 Validator Compensation
Since the transition to Proof-of-Stake in September 2022, validators securing Ethereum are rewarded through:
- Block rewards: ~4-5% APR on their stake
- Priority fees: The tips you add to your transactions
- MEV (Maximal Extractable Value): Additional revenue from transaction ordering
How Does Gas Work on Ethereum?
Gas fee calculation relies on three components since EIP-1559 (August 2021): the gas limit, base fee, and priority fee. This major upgrade transformed the fee system, making it more predictable and deflationary.
🧮 The Three Gas Components
1. Gas Limit — The Maximum Quantity
The gas limit is the maximum gas you authorize for your transaction. It’s a protection: if an operation consumes more than expected (bug, congestion), it automatically stops at this limit.
- Simple ETH transfer: 21,000 gas (fixed, incompressible)
- ERC-20 token transfer: 50,000 – 65,000 gas
- Uniswap swap: 100,000 – 200,000 gas
- Contract deployment: 500,000 – 5,000,000+ gas
⚠️ Important: Unused gas limit is refunded! If you set 50,000 gas but your transaction only consumes 30,000, the remaining 20,000 is returned to you.
2. Base Fee — The Algorithmic Minimum Price
The base fee is automatically calculated by the protocol based on previous blocks’ congestion:
- If the last block was more than 50% full → base fee increases (up to +12.5%)
- If the block was less than 50% full → base fee decreases (up to -12.5%)
- This mechanism creates self-regulation of congestion
🔥 Crucial point: The base fee is entirely burned (destroyed). This ETH disappears forever from circulation, creating deflationary pressure on the total supply.
3. Priority Fee (Tip) — The Validator Tip
The priority fee is an optional bonus you add to incentivize validators to include your transaction quickly:
- 0-1 gwei: Slow transaction (5-30 minutes)
- 1-2 gwei: Standard speed (1-5 minutes)
- 3-5+ gwei: Fast transaction (30 seconds – 1 minute)
Unlike the base fee, the priority fee is paid to validators as a direct reward.
💡 Complete Calculation Formula
Total Fees = Gas Used × (Base Fee + Priority Fee)
Concrete example for an ETH transfer:
• Gas used: 21,000 units (fixed)
• Base Fee: 25 gwei (varies with congestion)
• Priority Fee: 2 gwei (your tip)
Calculation: 21,000 × (25 + 2) = 567,000 gwei
= 0.000567 ETH
= ~$1.70 (at $3,000/ETH)🔥 The Burning Mechanism (EIP-1559)
Since August 2021, over 4 million ETH have been burned through this mechanism — more than $12 billion at current values! During periods of high activity (bull runs, major NFT launches), Ethereum even becomes deflationary: more ETH is burned than created.
You can track burning in real-time at Ultrasound.money.
How Much Does Each Transaction Type Cost?
Costs vary considerably depending on operation complexity — from a simple $2 transfer to several hundred dollars for sophisticated DeFi operations during congestion.
| Operation Type | Gas Used (approx.) | Estimated Cost (30 gwei)* | Peak Cost (100 gwei)* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple ETH Transfer | 21,000 | ~$2 | ~$6 |
| ERC-20 Token Transfer | 65,000 | ~$6 | ~$20 |
| Token Approval | 45,000 | ~$4 | ~$14 |
| Uniswap Swap (simple) | 150,000 | ~$14 | ~$45 |
| Multi-hop Swap | 250,000 | ~$23 | ~$75 |
| LP Liquidity Add | 200,000 | ~$18 | ~$60 |
| NFT Mint (ERC-721) | 100,000 | ~$9 | ~$30 |
| Complex DeFi Interaction | 350,000 | ~$32 | ~$105 |
| Smart Contract Deployment | 1,500,000+ | ~$140+ | ~$450+ |
*Estimates based on ETH at $3,000. Actual fees vary with network congestion.
Why is Gas Sometimes So Expensive?
Fee spikes occur when transaction demand temporarily exceeds network capacity — creating a “bidding war” between users. Here are the main factors:
📈 Network Congestion
- Major NFT launches: Popular collections generate thousands of simultaneous transactions
- Airdrops: Everyone wants to claim at the same time
- Market volatility: Bull runs and crashes create rushes to decentralized exchanges
- New DeFi protocols: FOMO pushes users to interact immediately
💹 ETH Price
Fees are paid in ETH — if the price rises, your fees in dollars increase proportionally even if the gwei price stays stable.
⚡ Operation Complexity
Modern DeFi involves increasingly complex transactions: multi-swaps, flashloans, automated strategies… Each additional instruction consumes gas.
How to Reduce Your Gas Fees? 6 Effective Strategies
By optimizing your habits, you can save 70-95% on your annual fees. Here are the best strategies:
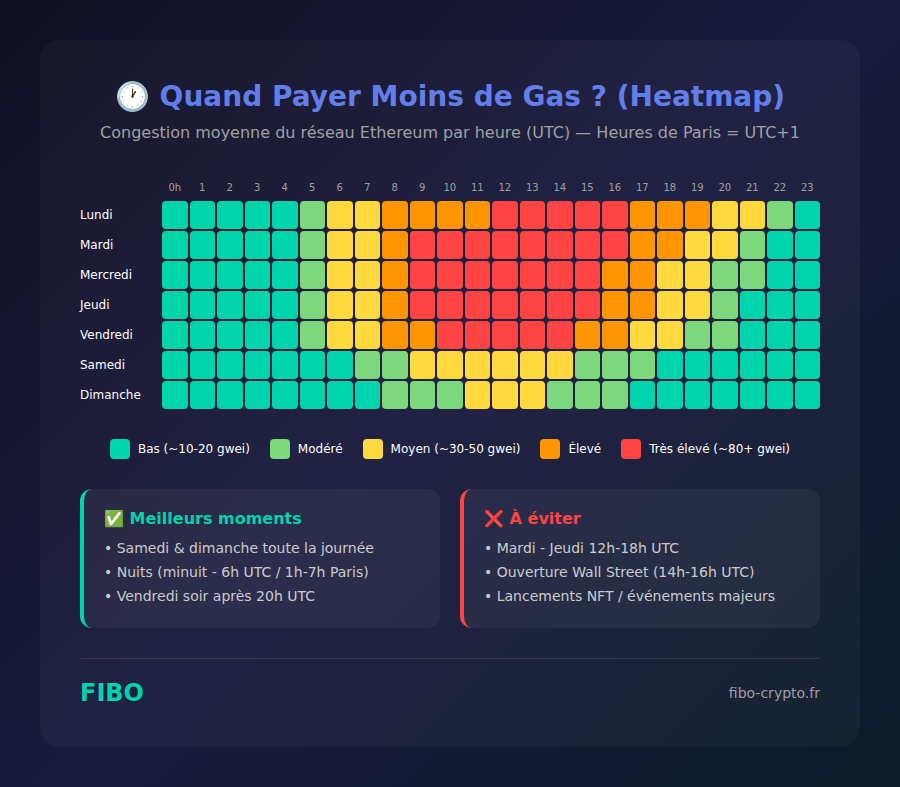
⏰ 1. Choose the Right Time (Timing)
Congestion follows predictable patterns tied to major market time zones:
- Ideal off-peak hours: Saturday-Sunday all day, nights (midnight-6am UTC)
- Avoid: Tuesday-Thursday 2pm-6pm UTC (Wall Street open + Europe active)
- Monitoring tools: Etherscan Gas Tracker, Blocknative, Gas.watch
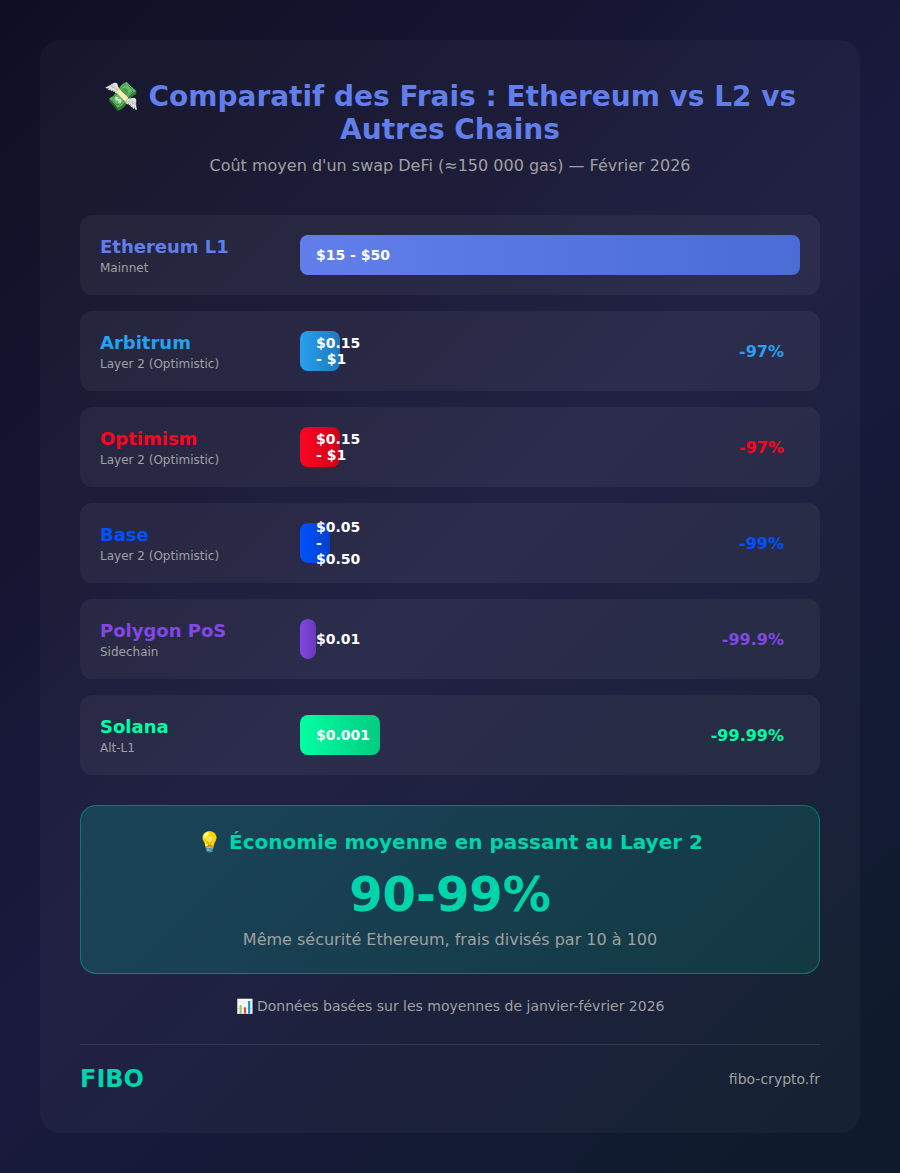
🌉 2. Use Layer 2s (90-99% savings)
Layer 2 solutions offer Ethereum’s security with fees divided by 10 to 100:
- Arbitrum: Most adopted, compatible with all Ethereum tools
- Optimism: Fast and economical, ideal for DeFi
- Base: Developed by Coinbase, ultra-low fees
- zkSync Era: zk-rollup technology, very promising
💡 Tip: Most popular dApps (Uniswap, Aave, Curve) are available on these L2s.
🔧 3. Batch Your Transactions
Some protocols allow executing multiple operations in a single transaction, dividing fixed costs.
📊 4. Set an Appropriate Gas Limit
Don’t excessively overestimate your gas limit — wallets like MetaMask provide reliable estimates. Too large a surplus might signal a problematic transaction to validators.
⏳ 5. Use Scheduled Transactions
Tools like Gelato Network allow you to automatically execute transactions when gas drops below a defined threshold.
🎯 6. Prioritize Intelligently
- Non-urgent: Minimal priority fee (0-1 gwei), wait for the next dip
- Standard: 1-2 gwei, processed in a few minutes
- Urgent: 3-5+ gwei, fast processing
Gas on Other Blockchains: Alternatives to Ethereum
Each blockchain has its own fee system with different trade-offs between cost, speed, and decentralization. Here’s an honest comparison:
| Blockchain | Average Fees | Speed | Security | Decentralization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethereum L1 | $2-50 | 12-15 sec | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Arbitrum (L2) | $0.10-1 | 2-5 sec | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Base (L2) | $0.01-0.50 | 2-5 sec | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Polygon PoS | $0.01-0.10 | 2 sec | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Solana | $0.0001-0.01 | 0.4 sec | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
| BNB Chain | $0.05-0.50 | 3 sec | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
| Avalanche C-Chain | $0.05-1 | 2 sec | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
💡 Our recommendation: For most users, Ethereum Layer 2s (Arbitrum, Base, Optimism) offer the best trade-off: very low fees + maximum security + full ecosystem compatibility.
The Future of Gas: 2026 Developments and Beyond
The future of gas looks revolutionary with several major innovations already transforming the user experience:
📦 Proto-Danksharding (EIP-4844) — Already Active
Deployed in March 2024, this upgrade introduces temporary data “blobs” that drastically reduce Layer 2 costs. Result: fees on Arbitrum/Optimism have been divided by 10 since then.
🧩 Full Danksharding — 2025-2026
The next step will divide the network into parallel “shards,” multiplying capacity by 10-100x. Goal: millions of transactions per second at negligible costs.
👤 Account Abstraction (ERC-4337) — Rolling Out
This innovation enables:
- Pay fees in stablecoins (USDC, DAI) instead of ETH
- Sponsored transactions: dApps can pay fees for you
- Social recovery: no more lost seed phrase = unrecoverable account
- Spending limits: enhanced security for new users
🚀 Long-term Vision
Ethereum’s goal for 2026-2030 is clear: make gas fees invisible to end users. Layer 2s will handle daily transactions at negligible costs, while mainnet remains the ultra-secure settlement layer.
📚 Glossary
- Gas : Unit measuring computational cost on Ethereum and EVM blockchains.
- Gwei : Sub-unit of ETH (1 gwei = 10⁻⁹ ETH = 0.000000001 ETH), used to express gas price.
- Wei : Smallest ETH unit (1 ETH = 10¹⁸ wei), rarely used directly.
- Gas Limit : Maximum amount of gas a user authorizes for a transaction. Unused surplus is refunded.
- Gas Price : Price per gas unit, expressed in gwei. Before EIP-1559, this was the only pricing parameter.
- Base Fee : Minimum price per gas unit since EIP-1559, automatically calculated based on congestion and entirely burned.
- Priority Fee (Tip) : Optional tip paid directly to validators to prioritize a transaction.
- EIP-1559 : Ethereum upgrade (August 2021) introducing base fee, burning mechanism, and more predictable fees.
- Burning : Permanent destruction of ETH via base fee, creating deflationary pressure.
- Layer 2 (L2) : Scalability solution built on top of Ethereum to reduce fees while inheriting its security.
- Optimistic Rollup : Type of Layer 2 (Arbitrum, Optimism) assuming transactions valid by default, with challenge period.
- ZK-Rollup : Type of Layer 2 (zkSync, StarkNet) using zero-knowledge cryptographic proofs for instant validation.
- EVM : Ethereum Virtual Machine, smart contract execution environment compatible with many blockchains.
- Nonce : Sequential transaction number for an account, used to order transactions and cancel pending ones.
- Proto-Danksharding (EIP-4844) : 2024 upgrade introducing data “blobs” to reduce L2 costs.
- Account Abstraction (ERC-4337) : Standard enabling stablecoin fee payment and sponsored transactions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do my gas fees vary so much from day to day?
Fees fluctuate based on Ethereum network congestion. During a popular NFT launch, major airdrop, or market crash, thousands of transactions are sent simultaneously. The base fee automatically adjusts upward to regulate this demand. Conversely, during quiet periods (weekends, nights), fees decrease significantly because fewer users are active.
Unfortunately, you still lose the gas fees. Validators performed computational work to attempt to execute your transaction (verifications, calculations), and this work must be compensated even if the operation doesn’t succeed. That’s why it’s crucial to verify all parameters before sending: sufficient slippage, adequate gas limit, and token approvals completed.What happens if my Ethereum transaction fails?
Gas limit represents the maximum gas authorized (in units), while gas price (base fee + priority fee) is the price per gas unit (in gwei). Total cost = gas used × gas price. Important: unused gas limit is automatically refunded, so setting a higher limit doesn’t cost you more if the transaction doesn’t use it all.What's the difference between gas limit and gas price?
Yes, considerably! A transaction costing $50 on Ethereum L1 can cost less than $0.50 on Arbitrum or Optimism — a 90-99% reduction. These savings are made possible by bundling hundreds of transactions into “rollups” before publishing to mainnet. Since EIP-4844 (Proto-Danksharding), L2 fees have been divided by another 10.Are Layer 2s like Arbitrum really cheaper?
Gwei (giga-wei) is a sub-unit of ETH convenient for expressing gas prices. 1 ETH = 1,000,000,000 gwei (1 billion). Saying “30 gwei” is simpler than “0.00000003 ETH.” Wei is the smallest unit (1 ETH = 10¹⁸ wei). To convert: if you pay 50 gwei for 21,000 gas, the total cost is 50 × 21,000 = 1,050,000 gwei = 0.00105 ETH.What exactly is a gwei? How do I convert it?
Yes, by sending a new transaction with the same nonce, a higher priority fee, and 0 ETH to your own address. This transaction will “override” the old one if processed first. Most wallets (MetaMask, etc.) offer a “Speed Up” or “Cancel” button that does exactly this. Note: you’ll pay fees for this cancellation.Can I cancel a pending Ethereum transaction?
With account abstraction (ERC-4337), it becomes possible to pay fees in stablecoins (USDC, DAI) or benefit from transactions sponsored by dApps. This feature is progressively rolling out in 2025-2026. Some modern wallets like Argent or Safe already offer this option on Layer 2s.Can I pay gas fees with something other than ETH?
Fees are generally lowest during weekends (Saturday-Sunday) and nights (midnight-6am UTC). Avoid: Tuesday through Thursday between 2pm and 6pm UTC when Wall Street is open and Europe is still active. Use Etherscan Gas Tracker to monitor prices in real-time and plan your non-urgent transactions.What's the best time to transact on Ethereum?
📰 Sources
This article is based on the following sources:
- Official Ethereum Documentation – Gas
- EIP-1559 Specification
- EIP-4844 Proto-Danksharding
- Etherscan Gas Tracker
- L2Fees.info
- Ultrasound Money
- L2Beat
Comment citer cet article : Fibo Crypto. (2026). Ethereum Gas Fees Explained: Complete Guide to Transaction Costs (2026). Consulté le 11 February 2026 sur https://fibo-crypto.fr/en/blog/ethereum-gas-fees-transaction-guide


