DeFi: What Is Decentralized Finance? Complete Guide 2026

📋 Key Takeaways (TL;DR)
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance): An ecosystem of financial applications built on blockchain that operates without banks or intermediaries
- Available services: Lending, borrowing, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), yield farming, stablecoins, liquid staking — accessible 24/7/365
- TVL (Total Value Locked): Over $100 billion locked in DeFi protocols in 2026
- Key advantages: Permissionless, transparent, non-custodial, higher yields (3-15% APY vs 0.5% in traditional banks)
- Risks to know: Smart contract bugs, liquidations, impermanent loss, phishing, technical complexity
- Getting started: MetaMask wallet, buy some crypto, first tests on Layer 2 (Arbitrum, Polygon) with small amounts
- The future: Convergence with traditional finance (RWAs), MiCA regulation in Europe, growing institutional adoption
Imagine a financial world without banks, where loans are made automatically through computer programs, where you can exchange any asset 24 hours a day, and where you maintain total control of your money. This world already exists: it’s called DeFi, or decentralized finance.
DeFi today represents over $100 billion in total value locked across its protocols. It offers a concrete alternative to the traditional banking system: financial services that are accessible to everyone, without discrimination, without prior authorization, operating continuously. But what exactly is DeFi? How does it work? And most importantly, how can you benefit from it safely?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore every aspect of decentralized finance: from its fundamentals to practical applications, including its risks and the best strategies for getting started.
What Is DeFi? Definition and Core Principles
DeFi in One Sentence
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) refers to an ecosystem of financial applications built on public blockchains, primarily Ethereum. These applications use smart contracts to automate traditional financial services — lending, trading, insurance — without requiring intermediaries like banks.
In practice, instead of entrusting your money to a bank that decides who to lend it to, you interact directly with transparent and immutable computer programs. Code replaces the banker.
The 6 Fundamental Characteristics of DeFi
- Decentralization: No central entity controls the protocol. Decisions are made by the community through governance votes
- Permissionless: Anyone can use the services without authorization. No KYC, no bank account required
- Transparency: All code is open-source and verifiable. Every transaction is visible on the blockchain
- Composability: Protocols interconnect like “financial LEGOs.” A deposit on Aave can serve as collateral on another protocol
- Non-custodial: You maintain control of your funds at all times. No one can freeze your account
- Programmability: Financial rules are coded into self-executing smart contracts
DeFi vs Traditional Finance: The Complete Comparison
To understand the revolution that DeFi represents, let’s compare it point by point with the financial system we know.

| Criteria | Traditional Finance | DeFi |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Mandatory KYC, bank account required. 1.7 billion people excluded from the system | Accessible to anyone with just a crypto wallet |
| Hours | Business days only, closed weekends and holidays | 24/7/365 — operates continuously |
| Intermediaries | Banks, brokers, clearinghouses, T+2 delays | Automated smart contracts, instant settlement |
| Transparency | Opaque. Internal processes invisible | Total. Open-source code, on-chain verifiable transactions |
| Custody | Custodial — the bank holds your funds | Non-custodial — you maintain total control |
| Saver rates | Savings accounts: 0.01-1% | High-yield: 2-4% | Stablecoins: 3-8% APY | Yield farming: 5-20%+ |
| Innovation | Slow (regulations, legacy systems) | Fast (open-source, composability) |
| Main risks | Bank failures, account freezing, inflation | Smart contract bugs, volatility, complexity |
How Does DeFi Work? The Technical Architecture Explained
Smart Contracts: The Heart of DeFi
At the core of DeFi are smart contracts — computer programs that execute automatically on the blockchain when certain conditions are met. These contracts are:
- Immutable: once deployed, they cannot be modified (except through governance upgrades)
- Transparent: the code is visible to everyone on the blockchain
- Deterministic: they always produce the same result for the same inputs
- Self-executing: no human intervention needed for their operation
Concrete Example: A DeFi Loan on Aave
Here’s how a DeFi loan works step by step:
- Collateral deposit: You deposit 10 ETH as collateral into Aave’s smart contract
- Automatic calculation: The smart contract determines your borrowing capacity (typically 70-80% of the value)
- Borrowing: You can borrow up to 7-8 ETH worth of stablecoins (USDC, DAI)
- Automatic interest: Interest accumulates every second according to a predefined algorithm based on supply and demand
- Monitoring: The protocol continuously monitors your collateralization ratio
- Automatic liquidation: If ETH price drops too much and your collateral becomes insufficient, the smart contract automatically liquidates your position to protect lenders
This entire process happens without any human intervention, no banker, no paperwork, in minutes instead of days.
Oracles: The Bridge to the Real World
Blockchains cannot directly access external world data (asset prices, exchange rates, etc.). Oracles like Chainlink serve as bridges by providing reliable data to smart contracts.
For example, to determine if your collateral is sufficient, Aave needs to know the current ETH price. Chainlink aggregates prices from numerous sources (Binance, Coinbase, etc.) and transmits them to the smart contract securely.
Main Categories of DeFi Protocols
The DeFi ecosystem is vast and diverse. Here are the main categories of available services.
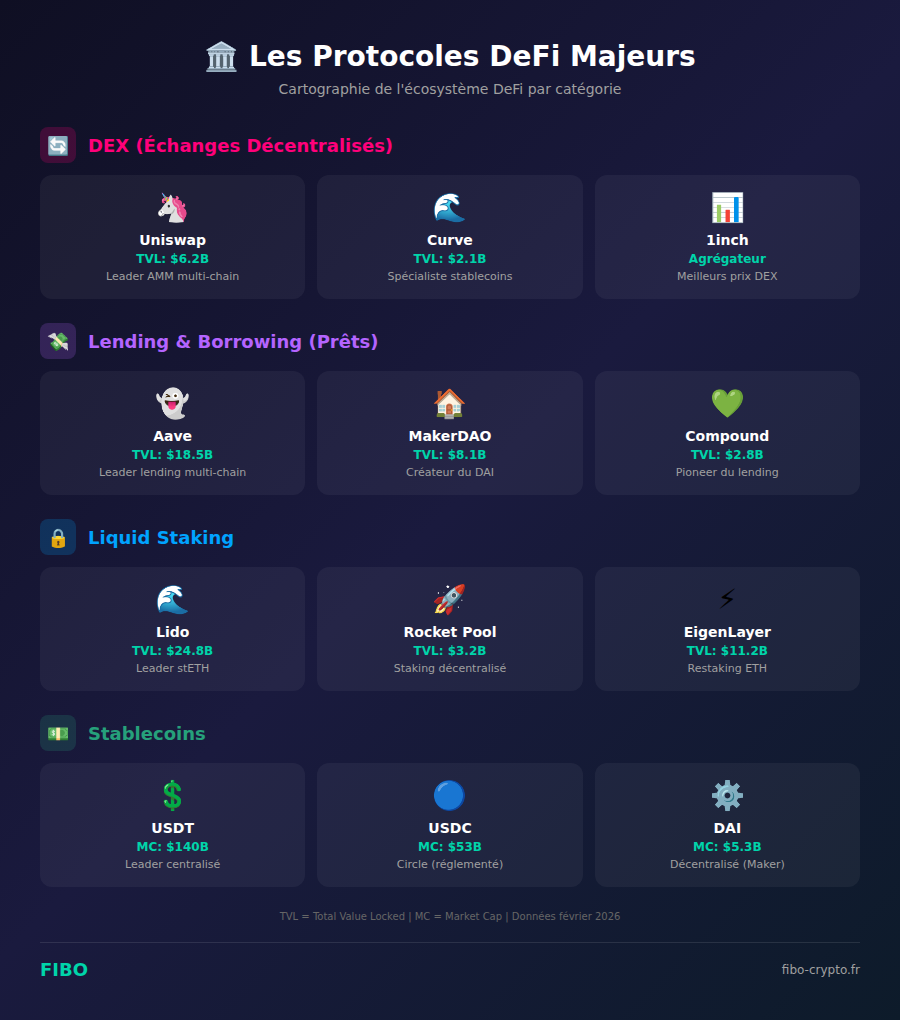
1. DEXs (Decentralized Exchanges)
DEXs allow you to swap cryptocurrencies directly from wallet to wallet, without going through a centralized platform like Binance or Coinbase.
How it works: Unlike traditional exchanges that use order books, most DEXs operate with AMMs (Automated Market Makers) — algorithms that determine prices from liquidity pools.
Major DEXs:
- Uniswap (TVL: $6.2B): Historic leader, classic AMM model, multi-chain
- Curve Finance (TVL: $2.1B): Specialized in stablecoin swaps with very low slippage
- PancakeSwap: Main DEX on BNB Chain
- 1inch: Aggregator that finds the best prices by comparing all DEXs
2. Lending & Borrowing
Lending protocols allow you to lend your crypto to earn interest, or borrow by depositing collateral.
Major protocols:
- Aave (TVL: $18.5B): Undisputed leader, flash loans, multi-chain, variable/stable rates
- Compound (TVL: $2.8B): Pioneer of algorithmic lending, creator of the cToken model
- MakerDAO (TVL: $8.1B): Creator of the DAI stablecoin, CDP (Collateralized Debt Positions) system
3. Yield Farming & Liquidity Mining
Yield farming involves optimizing returns by using multiple DeFi protocols. “Yield farmers” move their funds between protocols to maximize APY.
Liquidity mining is a form of yield farming where protocols distribute their native tokens to users who provide liquidity, creating additional incentives.
Popular protocols:
- Yearn Finance: Automated yield aggregator — deposit your crypto and strategies optimize automatically
- Convex Finance: Curve yield optimization without token locking
- Pendle Finance: Allows you to separate and trade the future yield of your assets
4. Decentralized Stablecoins
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies whose value is pegged to a fiat currency (usually the dollar). They serve as a safe haven and medium of exchange in the DeFi ecosystem.
Types of stablecoins:
- Centralized: USDT ($140B), USDC ($53B) — backed by dollar reserves
- Decentralized over-collateralized: DAI ($5.3B) — created by depositing crypto as collateral
- Hybrid/Algorithmic: FRAX, crvUSD — partially algorithmic stabilization mechanisms
5. Liquid Staking
Liquid staking allows you to stake your ETH to secure the Ethereum network while maintaining liquidity. In exchange for your staked ETH, you receive a derivative token (stETH, rETH) that you can use in other DeFi protocols.
Major protocols:
- Lido (stETH) (TVL: $24.8B): Absolute leader with ~30% of staked ETH
- Rocket Pool (rETH) (TVL: $3.2B): More decentralized alternative with independent node operators
- EigenLayer (TVL: $11.2B): Restaking — use your staked ETH to secure other protocols and multiply yields
6. Derivatives & Options
DeFi also enables trading of decentralized derivatives:
- dYdX: Decentralized perpetuals trading
- GMX: Perpetuals with innovative liquidity model
- Synthetix: Creation of synthetic assets (stocks, forex, commodities)
The History of DeFi: From Bitcoin to Today
Decentralized finance didn’t emerge overnight. It’s the result of over 15 years of successive innovations.
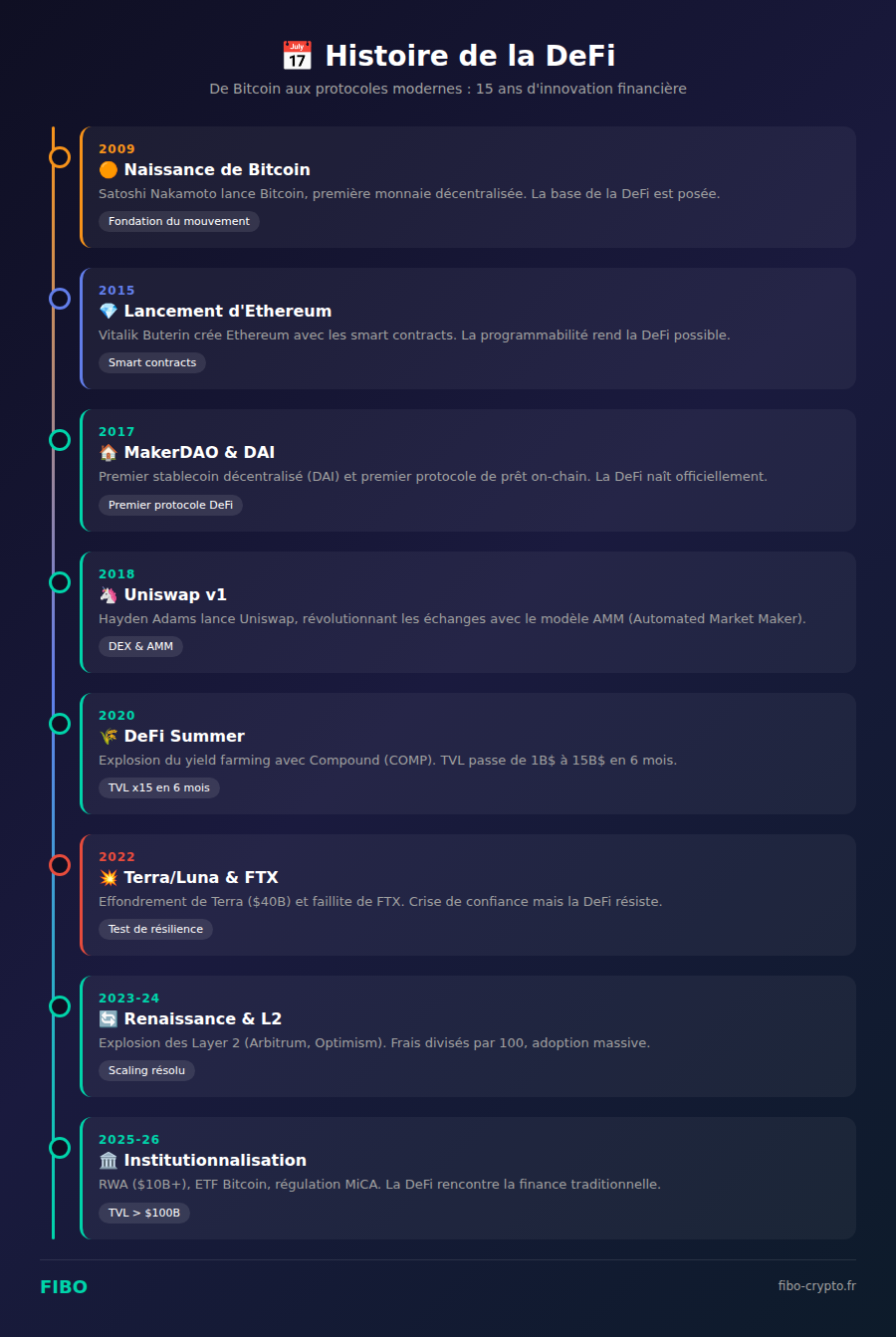
2009-2014: Foundations with Bitcoin
Bitcoin laid the groundwork for decentralized finance by proving that money can function without a central authority. However, Bitcoin remained limited: it couldn’t create complex financial applications.
2015: Ethereum Changes Everything
The launch of Ethereum introduced smart contracts, enabling any financial logic to be programmed on the blockchain. DeFi became technically possible.
2017: Birth of MakerDAO
MakerDAO launched DAI, the first decentralized stablecoin, and the first true DeFi protocol. Users could borrow DAI by depositing ETH as collateral.
2018: Uniswap Arrives
Hayden Adams created Uniswap, revolutionizing exchanges with the AMM model. No more order books needed: anyone could swap tokens instantly.
2020: The “DeFi Summer”
Compound launched its COMP token and inaugurated liquidity mining. The yield farming explosion propelled TVL from $1 billion to $15 billion in 6 months. DeFi entered the crypto mainstream.
2021: The Euphoria
TVL reached $180 billion at its peak. New protocols emerged every week. NFTs and DeFi intersected. Everyone talked about “money legos.”
2022: The Crash and Resilience
The collapse of Terra/Luna ($40B evaporated) and FTX bankruptcy shook the ecosystem. TVL dropped to $40B. But DeFi protocols proved resilient: Uniswap, Aave, MakerDAO continued operating without interruption, proving the resilience of decentralization.
2023-2024: Renaissance and Scaling
The explosion of Layer 2s (Arbitrum, Optimism, Base) divided fees by 100x and made DeFi accessible to small portfolios. Bitcoin and Ethereum ETF approvals marked institutional entry.
2025-2026: Institutionalization
Convergence between DeFi and traditional finance accelerates with RWAs (Real World Assets) — tokenization of bonds, real estate, private credit. MiCA regulation in Europe provides a legal framework. TVL surpasses $100 billion again.
DeFi by the Numbers: Key Statistics 2026

Some figures to measure the scale of the DeFi ecosystem:
- Total TVL: $102 billion
- Active protocols: 3,500+
- Supported blockchains: 100+
- Monthly active wallets: 10+ million
- Daily DEX volume: $2+ billion
- Stablecoin market cap: $200+ billion
- ETH in liquid staking: $38 billion
Advantages of DeFi: Why It’s Revolutionizing Finance
1. Universal Financial Inclusion
1.7 billion people worldwide lack access to banking services. DeFi opens doors for them: a smartphone and internet connection are enough to save, borrow, and invest.
2. Superior Yields
While traditional savings accounts offer less than 1%, DeFi enables 3-8% on stablecoins with moderate risk, and much more for advanced strategies.
3. Total Transparency
Every transaction, every line of code is publicly verifiable. It’s impossible for a protocol to “create money secretly” as banks can do through fractional reserve banking.
4. Total Control of Your Assets
In DeFi, your keys, your crypto. No bank can freeze your account, no government can seize your funds (as long as you secure your private keys).
5. Continuous Innovation
Open-source and composability enable rapid innovation. New financial products impossible in TradFi emerge regularly: flash loans, yield tokenization, restaking…
6. 24/7 Accessibility
No more weekend closures. No more waiting for wire transfers. DeFi operates continuously, anywhere in the world.
DeFi Risks: What You Need to Know
DeFi offers exceptional opportunities, but it also carries significant risks that you must understand before getting involved.
Technical Risks
- Smart contract bugs: A bug in the code can result in total loss of funds. In 2022, the Wormhole protocol lost $320M due to a vulnerability.
- Oracle attacks: Manipulation of prices provided by oracles can be exploited by attackers.
- Flash loan attacks: Sophisticated exploits using instant loans to manipulate protocols.
- Implementation bugs: Even audited code may contain flaws discovered later.
Financial Risks
- Impermanent loss: Liquidity providers can suffer losses when asset prices diverge.
- Liquidations: If your collateral loses too much value, your position will be automatically liquidated, sometimes with penalties.
- Stablecoin depeg: A stablecoin can lose its $1 peg, as demonstrated by UST’s collapse.
- Yield volatility: APYs can drop sharply when incentives decrease.
User Risks
- Sending errors: Sending funds to the wrong address is irreversible.
- Malicious approvals: Approving a malicious smart contract can drain your wallet.
- Phishing: Fake DeFi sites are numerous. One character error in the URL can be costly.
- Lost seed phrase: Losing your recovery phrase = losing all your funds permanently.
How to Get Started with DeFi: Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Set Up Your Wallet
You’ll need a non-custodial Web3-compatible wallet. Here are the recommended options:
- MetaMask: Most popular, browser extension + mobile app
- Rabby Wallet: Better multi-chain management, built-in security alerts
- Rainbow: Elegant interface, ideal for mobile beginners
- Ledger/Trezor: Hardware wallets for maximum security (recommended for large amounts)
⚠️ Golden rule: Write down your seed phrase on paper, never as a photo or online. It’s the key to all your funds.
Step 2: Buy Crypto
- Create an account on a buying platform (Coinbase, Kraken, Binance)
- Buy ETH or stablecoins (USDC)
- Transfer to your MetaMask wallet
- Make sure you have “gas” (ETH on Ethereum, ETH/MATIC on L2s)
Step 3: Choose the Right Blockchain
Fees on Ethereum mainnet can be prohibitive ($5-50 per transaction). For starting with small amounts, prioritize Layer 2s:
- Arbitrum: Large DeFi ecosystem, fees ~$0.10-0.50
- Optimism: Good liquidity, similar fees
- Polygon: Very low fees (~$0.01), ideal for testing
- Base: By Coinbase, rapidly growing
Step 4: Secure First Steps
- Start with SMALL amounts: $50-100 maximum for learning
- Use established protocols: Uniswap, Aave, Curve — no unaudited new projects
- ALWAYS verify the URL: Bookmark official sites (app.uniswap.org, aave.com)
- Avoid unlimited approvals: Only approve the necessary amount
- Regularly revoke old approvals on revoke.cash
Recommended Beginner Strategy: Stablecoin Lending
Here’s a simple, relatively low-risk first strategy:
- Buy $100-500 USDC
- Transfer to Arbitrum (via official bridge)
- Deposit on Aave (app.aave.com)
- Earn ~4-7% APY passively
- Withdraw whenever you want (instant liquidity)
Advanced DeFi Strategies to Maximize Returns
Once familiar with the basics, here are strategies used by experienced users.
1. Liquidity Providing (LP)
Provide liquidity to a DEX by depositing two tokens in a pool. You earn a portion of trading fees. Beware of impermanent loss if token prices diverge.
2. Rotational Yield Farming
Move your funds to protocols offering the best yields. Aggregators like Yearn automate this process.
3. Leveraged Farming
Borrow against your collateral to reinvest and amplify returns. High liquidation risk — reserved for experts.
4. Liquid Staking + DeFi
Stake your ETH via Lido (receive stETH), then use that stETH as collateral on Aave. Double yield: staking + lending.
5. Points Farming
Participate in protocols distributing “points” before their token airdrop. Popular strategy in 2024-2026.
The Future of DeFi: Trends and Outlook 2026-2030
Real World Assets (RWAs)
Tokenization of real-world assets (bonds, real estate, private credit) represents the next frontier. Protocols like Centrifuge, Maple Finance, and Goldfinch already allow investing in traditional assets via DeFi.
Convergence with TradFi
Traditional financial institutions are beginning to adopt blockchain technology. BlackRock launched a tokenized fund on Ethereum. JPMorgan experiments with Onyx. The boundary between DeFi and TradFi is blurring.
Regulation
The MiCA regulation in Europe provides a legal framework for crypto-assets. DeFi protocols may need to adapt, but this clarification also promotes institutional adoption.
Account Abstraction
New standards (ERC-4337) enable simpler-to-use wallets: social recovery, paying fees in stablecoins, automated transactions. DeFi UX is improving dramatically.
Conclusion: DeFi, a Financial Revolution in Progress
Decentralized finance represents much more than a simple technological innovation: it’s a complete overhaul of our relationship with money and financial services. For the first time in history, anyone can access sophisticated financial services without the permission of a bank or government.
Certainly, DeFi remains a young field with real risks. Bugs, hacks, and technical complexity are all obstacles to overcome. But the fundamentals are solid: transparency, decentralization, universal accessibility.
Our advice: Start small, learn gradually, and never risk more than you can afford to lose. DeFi isn’t a casino — it’s a powerful new financial tool for those who take the time to understand it.
📚 Glossary
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance): Ecosystem of financial applications on blockchain operating without centralized intermediaries like banks.
- Smart contract: Autonomous program on blockchain that automatically executes predefined financial rules when certain conditions are met.
- TVL (Total Value Locked): Total value of assets deposited in a DeFi protocol, a key indicator of its adoption and health.
- DEX (Decentralized Exchange): Cryptocurrency exchange platform operating without a centralized intermediary, directly wallet to wallet.
- AMM (Automated Market Maker): Algorithm that automatically determines asset prices on a DEX via liquidity pools.
- Collateral: Assets deposited as security to borrow in a DeFi lending protocol.
- Stablecoin: Cryptocurrency pegged to a fiat currency (USDC, DAI, USDT pegged to the US dollar).
- Yield farming: Strategy of optimizing returns by moving funds between different DeFi protocols.
- Impermanent loss: Temporary loss suffered by liquidity providers when pool asset prices diverge.
- Liquidation: Forced automatic sale of a borrower’s collateral when its value becomes insufficient to cover the loan.
- Oracle: Service providing real-world data (asset prices) to smart contracts reliably and securely.
- Wallet: Interface for storing cryptocurrencies and interacting with DeFi protocols.
- Layer 2: Scalability solution built on top of Ethereum to reduce fees and increase speed (Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon).
- APY (Annual Percentage Yield): Compound annual interest rate, including interest on interest.
- Permissionless: Characteristic of a system open to all without requiring authorization or identity verification.
- Non-custodial: System where the user maintains total control of their private keys and thus their funds.
- Liquidity pool: Reserve of tokens deposited by users in a smart contract to facilitate exchanges on a DEX.
- Gas: Fees paid to execute transactions on a blockchain (expressed in Gwei on Ethereum).
- Flash loan: Instant loan without collateral that must be repaid within the same blockchain transaction.
- Governance token: Token giving voting rights to influence DeFi protocol decisions (UNI, AAVE, CRV).
Frequently Asked Questions
Is DeFi safe for investing?
DeFi carries specific risks: smart contract bugs, hacks, cryptocurrency volatility. However, established protocols like Aave, Uniswap, or MakerDAO have proven their resilience over several years of operation with billions of dollars in TVL. To minimize risks: only use audited protocols, start with small amounts, diversify across multiple protocols, and never deposit more than you can afford to lose.
How can a beginner invest in DeFi?
To get started: 1) Create a MetaMask or Rabby wallet, 2) Buy crypto on a regulated platform (Coinbase, Kraken), 3) Transfer to your wallet, 4) Start with stablecoin lending on Aave — it’s the simplest strategy with moderate risk. Use a Layer 2 like Arbitrum or Polygon to reduce fees. Start with $50-100 to familiarize yourself before increasing amounts.
What returns are possible in DeFi?
Returns vary by strategy and risk: stablecoin lending offers 3-8% APY (low risk), liquidity provision 5-20% APY (medium risk with impermanent loss), aggressive yield farming can reach 20-100%+ APY (high risk). Beware of abnormally high yields: they often signal hidden risks or protocols that aren’t sustainable long-term.
Is DeFi legal?
Yes, using DeFi is legal in most countries including the US, UK, and EU. The MiCA regulation (2024) progressively regulates crypto-assets in Europe. Realized gains are taxable: in the US, crypto profits are subject to capital gains tax. Consult a tax professional for your specific situation.
What is impermanent loss and how to avoid it?
Impermanent loss is the loss suffered by liquidity providers when the prices of two tokens in a pool diverge. The greater the divergence, the larger the loss. It becomes ‘permanent’ if you withdraw liquidity at that point. To minimize: favor stablecoin pools (USDC/USDT), choose correlated pairs, or use protocols with impermanent loss protection (Bancor v3, certain Uniswap v3 pools).
What’s the difference between a DEX and a centralized exchange?
A centralized exchange (Binance, Coinbase) holds your funds and acts as intermediary for each transaction. A DEX (Uniswap, Curve) allows direct wallet-to-wallet swaps via smart contracts — you maintain control of your crypto. DEXs offer more privacy and autonomy but may have less liquidity and a more complex interface for beginners.
How do I protect my wallet from DeFi scams?
Essential rules: 1) ALWAYS verify site URLs (phishing is very common), 2) Bookmark official protocol sites, 3) Never approve unlimited amounts to smart contracts, 4) Regularly revoke old approvals on revoke.cash, 5) Never click links in DMs or emails, 6) Use a hardware wallet (Ledger) for large amounts, 7) Enable Rabby extension that alerts on suspicious transactions.
What is liquid staking and why is it popular?
Liquid staking allows you to stake ETH to secure Ethereum while receiving a liquid token (stETH, rETH) in exchange. This token represents your staked ETH + accumulated rewards. The advantage: you can use this token in other DeFi protocols (as collateral on Aave) for additional yields. It’s become the largest DeFi category with over $38 billion in TVL.
What are the best DeFi protocols in 2026?
The most established and reliable protocols in 2026: Aave (lending, $18.5B TVL), Lido (liquid staking, $24.8B TVL), Uniswap (DEX, $6.2B TVL), MakerDAO (DAI stablecoin, $8.1B TVL), Curve (stablecoin swaps, $2.1B TVL). These protocols have proven their resilience over several years, been audited numerous times, and manage billions in value.
Will DeFi replace banks?
DeFi probably won’t entirely replace banks, but it’s already transforming the financial landscape. We’re seeing convergence: banks are adopting blockchain (JPMorgan Onyx, BlackRock tokenized funds), while DeFi is institutionalizing. The future will likely be hybrid, with users choosing between traditional and decentralized services based on their needs. DeFi will excel in transparency, global accessibility, and innovation, while TradFi will retain advantages in consumer protection and personalized services.
📰 Sources
This article is based on the following sources:
- DeFi Llama
- Ethereum.org – DeFi
- Aave Documentation
- Uniswap Documentation
- Chainlink
- Messari Research
- L2Beat
- Dune Analytics
How to cite this article: Fibo Crypto. (2026). DeFi: What Is Decentralized Finance? Complete Guide 2026. Retrieved February 10, 2026 from https://fibo-crypto.fr/blog/defi-decentralized-finance-guide
