How Many Bitcoins Are There? Total Supply, Mining & Scarcity Explained

📅 Last updated: February 2026
📋 En bref (TL;DR)
- Absolute limit: 21 million bitcoins maximum — not one more, it’s written in the code
- Already mined: ~19.8 million BTC in circulation (94% of total)
- Remaining: ~1.2 million BTC to be created by 2140
- Halving: Mining rewards are cut in half every ~4 years, slowing creation
- Lost bitcoins: 3-4 million BTC forever inaccessible (lost keys, forgotten wallets)
- After 2140: No more creation, but the network continues via transaction fees
How Many Bitcoins Can Be Created in Total?
21 million. Not one more.
This is the limit set from the start by Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin’s creator. This limit is written into the protocol’s source code and cannot be changed without consensus from the entire network — which is practically impossible.
🧠 Why a limit? To create a form of money that’s scarce, like gold. Unlike traditional currencies that central banks can print at will, Bitcoin has a fixed and predictable supply.
As of February 2026, approximately 19.8 million bitcoins have already been created. That leaves less than 1.2 million to be produced by the year 2140.
How Are Bitcoins Created?
New bitcoins aren’t printed like regular money. They are “mined“.
⛏️ What is mining?
It’s a process where powerful computers solve cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions on the network and add them to the blockchain.
As a reward for this work, miners receive new bitcoins — it’s the only way to create them.
This work is performed by miners around the world, who play an essential role in the security and decentralized operation of the network.
The Halving: Fewer and Fewer Bitcoins Created
Every time a miner adds a block of transactions to the blockchain (roughly every 10 minutes), they receive a bitcoin reward. But this reward decreases over time.
This is called the halving (or “halvening”):
- 2009: 50 BTC per block
- 2012: 25 BTC per block (1st halving)
- 2016: 12.5 BTC per block
- 2020: 6.25 BTC per block
- 2024: 3.125 BTC per block
- 2028: 1.5625 BTC per block (expected)
- …
- ~2140: 0 BTC per block (end of creation)
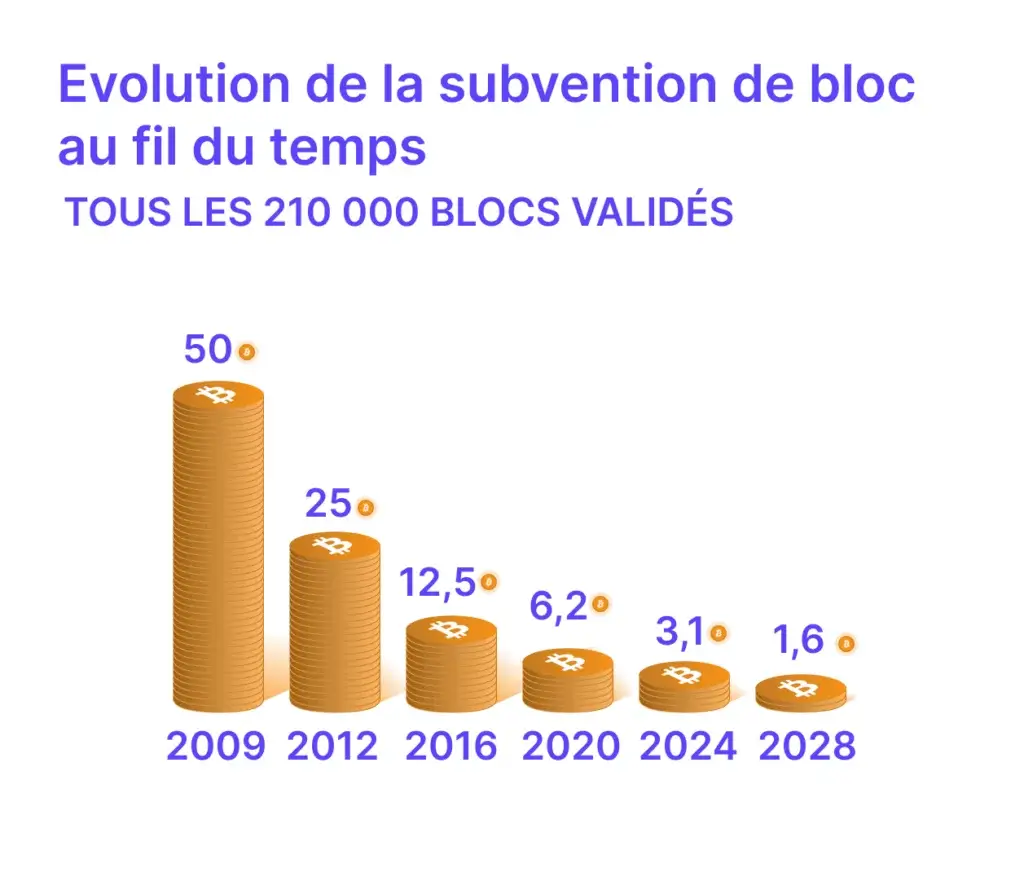
🔁 Every 210,000 blocks (~4 years), the number of new bitcoins created is cut in half. This makes new bitcoins increasingly scarce, which can contribute to increasing their value.
How Many Bitcoins Are Left to Mine?
There are approximately 1.2 million bitcoins left to create (as of February 2026).
But here’s the catch: because of the halving, it will take over 100 years to produce them all. The very last fraction of bitcoin (one satoshi) should be mined around the year 2140.
Here’s the emission progression:
- 2012: 50% of bitcoins created (10.5 million)
- 2016: 75% created (15.75 million)
- 2020: 87.5% created (18.375 million)
- 2024: 93.75% created (19.6875 million)
- 2028: 96.875% created
- 2140: 100% (21 million)
Lost Bitcoins: Making Bitcoin Even Scarcer
Not all created bitcoins are actually in circulation. It’s estimated that 3 to 4 million bitcoins are lost forever (15-20% of total supply).
❌ A bitcoin is “lost” when:
- The private key was deleted or forgotten
- The wallet was deleted without backup
- The owner died without passing on access
- Bitcoins were sent to an invalid address (burned)
These bitcoins can never be used again. It’s like throwing gold bars to the bottom of the ocean.
📉 Famous examples of lost bitcoins:
- James Howells: 8,000 BTC on a hard drive thrown in a landfill (current value: ~$800M)
- Stefan Thomas: 7,002 BTC on an IronKey whose password he forgot
- Satoshi Nakamoto: ~1.1 million BTC never moved since 2009
Fewer available bitcoins = more scarcity. This reinforces the idea that Bitcoin is a limited and potentially valuable asset.
Impact on Value: The Economics of Scarcity
A scarce asset, especially if in demand, tends to appreciate in value. Here are the consequences of this 21 million limit:
- ✅ Anti-inflation: Unlike euros or dollars printed at will, Bitcoin’s supply is fixed and predictable
- 📈 Limited supply: If demand increases and supply remains fixed, the price rises mechanically
- 🛡️ Store of value: This scarcity attracts investors seeking protection against inflation, like gold
💡 The Stock-to-Flow Model
This model compares existing stock (bitcoins in circulation) to production flow (newly mined bitcoins). The higher the ratio, the scarcer the asset. After the 2024 halving, Bitcoin has a higher S2F ratio than gold.
But be careful: bitcoin’s price can also be very volatile, as it depends on economic events, regulations, adoption, and market sentiment.
What Happens After 2140?
In 2140, all bitcoins will have been mined. No new ones will ever be created. But that doesn’t mean the system will stop!
The Network Will Keep Running
Even without new block rewards, miners will continue to validate transactions through transaction fees paid by users. These fees already exist today and will become miners’ sole compensation.
Bitcoins Will Be Even Scarcer
There will never be new bitcoins again. With ongoing losses (lost keys, deaths…), the actual supply will only decrease. This could strengthen their value if Bitcoin remains useful and in demand.
New Technologies
Solutions like the Lightning Network (for fast, near-free payments) already help reduce pressure on the main blockchain and associated fees.
Bitcoin vs Traditional Currencies: The Key Difference
The fundamental difference between Bitcoin and traditional currencies (euros, dollars) lies in their monetary policy:
- Fiat currencies: Unlimited supply, controlled by central banks that can “print” money (quantitative easing)
- Bitcoin: Fixed supply at 21 million, programmed and immutable
Since 2008, central banks have created trillions of dollars/euros, diluting savings value. Bitcoin was created precisely in response to this policy — the message in Bitcoin’s genesis block references bank bailouts.
Summary
- 🎯 21 million maximum — limit decided at Bitcoin’s creation
- ⛏️ Mining — creates new bitcoins and secures the network
- 🔁 Halving — cuts rewards in half every ~4 years
- 💸 ~19.8 million — already created (94% of total)
- ❌ 3-4 million lost — making remaining bitcoins even scarcer
- 🔮 After 2140 — no more creation, but the network continues via fees
Bitcoin is not like other currencies. Its fixed limit of 21 million makes it a scarce asset by design. Understanding this limit means understanding the very essence of Bitcoin and why it’s often compared to “digital gold.”
📚 Glossary
- Bitcoin : The first decentralized cryptocurrency, created in 2009. Its supply is limited to 21 million units.
- Satoshi Nakamoto : Pseudonym of Bitcoin’s anonymous creator, who set the 21 million limit.
- Mining : The process of validating transactions by computers that receive bitcoins as rewards.
- Miner : A person or company that participates in mining by providing computing power to the network.
- Blockchain : A decentralized, immutable ledger where all Bitcoin transactions are recorded.
- Block : A set of validated transactions added to the blockchain roughly every 10 minutes.
- Halving : A programmed event that cuts miner rewards in half every 210,000 blocks (~4 years).
- Satoshi : The smallest unit of Bitcoin (0.00000001 BTC). 1 BTC = 100 million satoshis.
- Private key : A secret code that grants access to your bitcoins. Losing it means permanently losing your funds.
- Wallet : A digital wallet for storing and managing bitcoins via cryptographic keys.
- Transaction fees : Amount paid to miners to include a transaction in a block.
- Lightning Network : A “layer 2” payment network enabling instant, near-free Bitcoin transactions.
- Genesis block : The first block of the Bitcoin blockchain, mined by Satoshi Nakamoto on January 3, 2009.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why exactly 21 million and not another number?
Satoshi Nakamoto never explained this specific choice. Several theories exist: it’s a round number in terms of satoshis (2.1 quadrillion), it allows for practical division with halvings, or it’s simply an arbitrary choice but small enough to create scarcity while allowing divisibility.
Can the 21 million limit be changed?
Technically, it would require near-unanimous consensus from all network nodes to modify this rule. In practice, it’s considered impossible because it would destroy Bitcoin’s fundamental value proposition. Any attempt would create a fork (a new cryptocurrency).
What will 1 bitcoin be worth when all 21 million are mined?
Impossible to predict. If Bitcoin remains used and in demand with a fixed (or even decreasing due to losses) supply, economic theory suggests price appreciation. But this depends on adoption, regulation, and competition from other technologies.
Will miners be profitable after 2140?
Yes, they’ll be compensated solely by transaction fees. For the system to remain secure, these fees must be sufficient to cover mining costs. The Lightning Network and other Layer 2 solutions also help reduce dependence on the main blockchain.
How many people own 1 whole bitcoin?
It’s estimated there are only ~1 million addresses holding at least 1 BTC (some people have multiple addresses). With 21 million BTC maximum and 8 billion humans, there mathematically aren’t enough whole bitcoins for everyone.
Is Bitcoin really comparable to gold?
The analogy is relevant for scarcity: gold is limited on Earth, Bitcoin is limited to 21 million. But Bitcoin has advantages (divisibility, portability, instant verifiability) and disadvantages (volatility, dependence on electricity/Internet) compared to gold.
📰 Sources
This article is based on the following sources:
- Bitcoin White Paper
- Bitcoin Source Code
- Clark Moody Bitcoin Dashboard
- Chainalysis – Lost Bitcoin Research
- Glassnode
Comment citer cet article : Fibo Crypto. (2026). How Many Bitcoins Are There? Total Supply, Mining & Scarcity Explained. Consulté le 4 February 2026 sur https://fibo-crypto.fr/en/blog/how-many-bitcoins-total-supply



