Crypto Staking: Complete Guide to Generating Passive Income in 2025

📋 En bref (TL;DR)
- Staking involves locking cryptocurrencies on a Proof of Stake blockchain to secure the network and receive rewards (3 to 12% APR). It’s an eco-friendly alternative to mining, accessible from just a few dollars via pools or exchanges. Be aware of the risks: volatility, lock-up periods, and slashing.
Introduction
Staking has established itself as one of the most popular methods for generating passive income in the cryptocurrency world. Since Ethereum’s transition to Proof of Stake in September 2022, this practice has experienced exponential growth: over $28 billion is currently staked on Ethereum alone. Unlike traditional mining, which requires expensive hardware and significant electricity consumption, staking allows anyone holding cryptocurrencies to participate in securing blockchain networks. In exchange for this contribution, participants receive regular rewards, typically expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR). This comprehensive guide will help you understand staking, from its technical mechanisms to practical strategies for maximizing your returns while managing the associated risks.

What Is Staking?
Staking is the process by which a cryptocurrency holder locks their tokens to participate in the operation of a Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain. In exchange for this contribution to network security, they receive rewards in the form of new tokens. The term “staking” comes from “stake,” meaning something put at risk as a guarantee. Essentially, you put your cryptocurrencies at stake to guarantee your good faith as a network validator. If you attempt to cheat or validate fraudulent transactions, you risk losing part of your stake (this is the slashing mechanism). Staking differs fundamentally from mining:
- Mining (Proof of Work): solving complex cryptographic puzzles requiring significant computing power
- Staking (Proof of Stake): locking tokens as collateral to earn the right to validate transactions
Among blockchains using Proof of Stake, you’ll find Ethereum (since The Merge), Solana, Cardano, Polkadot, Avalanche, Cosmos, and Tezos.
How Does Staking Work?
Staking is based on a four-step process: choose a PoS cryptocurrency, delegate or lock your tokens, participate in block validation via a validator, then receive rewards proportional to your contribution.
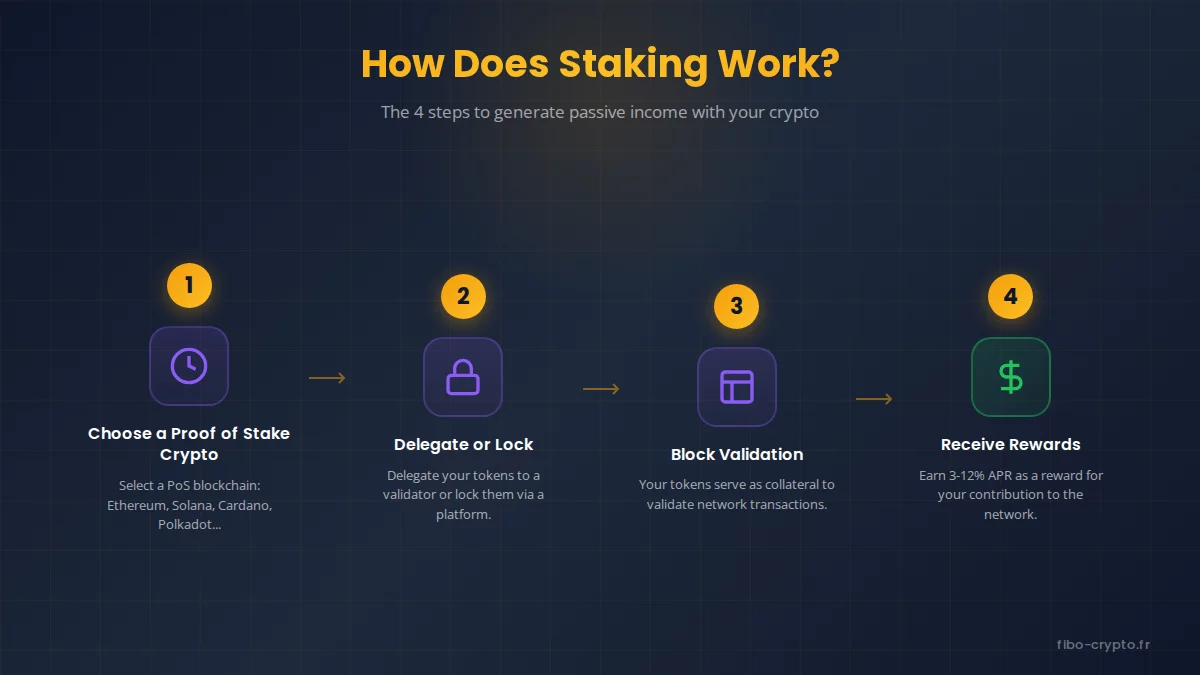
The Proof of Stake Mechanism
Proof of Stake is a consensus mechanism that selects validators in a pseudo-random manner, taking into account several factors:
- Amount staked: the more tokens you stake, the higher your chances of being selected
- Age: some protocols favor tokens that have been staked for longer periods
- Randomization: a random element ensures fairness in the system
Unlike Proof of Work where computing power determines who validates blocks, PoS uses token ownership as the selection mechanism. This makes the system approximately 99.95% less energy-intensive, according to the Ethereum Foundation.
The Role of Validators
Validators are the central actors in Proof of Stake. Their mission consists of:
- Verifying transactions: ensuring each transaction is legitimate and properly signed
- Proposing blocks: grouping validated transactions into a new block
- Attesting blocks: confirming that blocks proposed by other validators are valid
- Maintaining uptime: staying online 24/7 to not miss validation opportunities
On Ethereum, becoming a solo validator requires staking 32 ETH (approximately $80,000 at current prices) and running a node continuously. This is why most individuals opt for delegated staking solutions.
The 5 Staking Methods
There are five main approaches to staking your cryptocurrencies, each presenting a different balance between control, yield, and ease of use. From solo staking reserved for experts to exchange staking accessible to everyone, here’s the breakdown of each method.
1. Solo Staking
Solo staking involves running your own validator node. It’s the most decentralized method and offers the best returns (4-5% APR on Ethereum). Advantages:
- Full control over your funds
- Best returns (no intermediary fees)
- Maximum contribution to decentralization
Disadvantages:
- High minimum (32 ETH for Ethereum)
- Technical skills required
- Reliable hardware and internet connection necessary
2. Staking-as-a-Service (SaaS)
You own the 32 ETH but delegate the technical aspect to a professional operator who manages the node for you. You retain your withdrawal keys. Yield: 3-4% APR (after 10-25% service fees) Examples: Allnodes, Blox Staking, Staked.us
3. Pooled Staking
Multiple users combine their funds to reach the required minimum. Rewards are distributed proportionally to each participant’s contribution. Yield: 3-4% APR Advantages: Accessible without minimum, decentralized Examples: Rocket Pool (rETH), StakeWise
4. Liquid Staking
Liquid staking revolutionizes the ecosystem by allowing you to stake while maintaining liquidity. You receive a derivative token (stETH, rETH) representing your staked position, usable in DeFi. Yield: 3-4% APR + DeFi opportunities Major advantages:
- No unlock period
- Use in DeFi (collateral, yield farming)
- Accessible from just a few dollars
Main protocols: Lido (stETH), Rocket Pool (rETH), Coinbase (cbETH)
5. Exchange Staking
The simplest method: stake directly on a centralized exchange like Binance, Coinbase, or Kraken. Yield: 2-4% APR (after platform commission) Advantages: Ultra simple, familiar interface, customer support Disadvantages:
- Centralization (“not your keys, not your coins”)
- Counterparty risk
- Generally lower returns
Benefits and Risks of Staking
Staking offers attractive passive income opportunities with a low barrier to entry, but comes with specific risks that are crucial to understand before committing.

The 6 Benefits of Staking
- Regular passive income: generate 3 to 12% annual returns depending on the protocols
- Simplicity: no specialized hardware or advanced technical skills needed
- Network participation: contribute to the security and decentralization of blockchains
- Compound interest: automatically reinvest your rewards for exponential growth
- Ecological impact: PoS consumes 99.95% less energy than mining
- Accessibility: start with just a few dollars via liquid staking or exchanges
The 6 Risks of Staking
- Market volatility: your percentage returns don’t necessarily offset a price crash. A 5% APR is insignificant if the token loses 50% of its value.
- Lock-up period: your funds may be locked for days or weeks. On Ethereum, withdrawal delays vary depending on network queue.
- Slashing: if your validator commits a fault (double signing, extended downtime), part of your stake can be confiscated.
- Counterparty risk: centralized platforms can go bankrupt (remember FTX, Celsius, BlockFi). Prefer non-custodial solutions.
- Tax complexity: in most jurisdictions, staking rewards are taxable income upon receipt.
- Variable returns: APR fluctuates based on the total number of tokens staked on the network and market conditions.
Staking vs Other Yield Methods
Staking isn’t the only way to grow your cryptocurrencies. Let’s objectively compare it to mining and lending to help you choose the strategy suited to your profile.
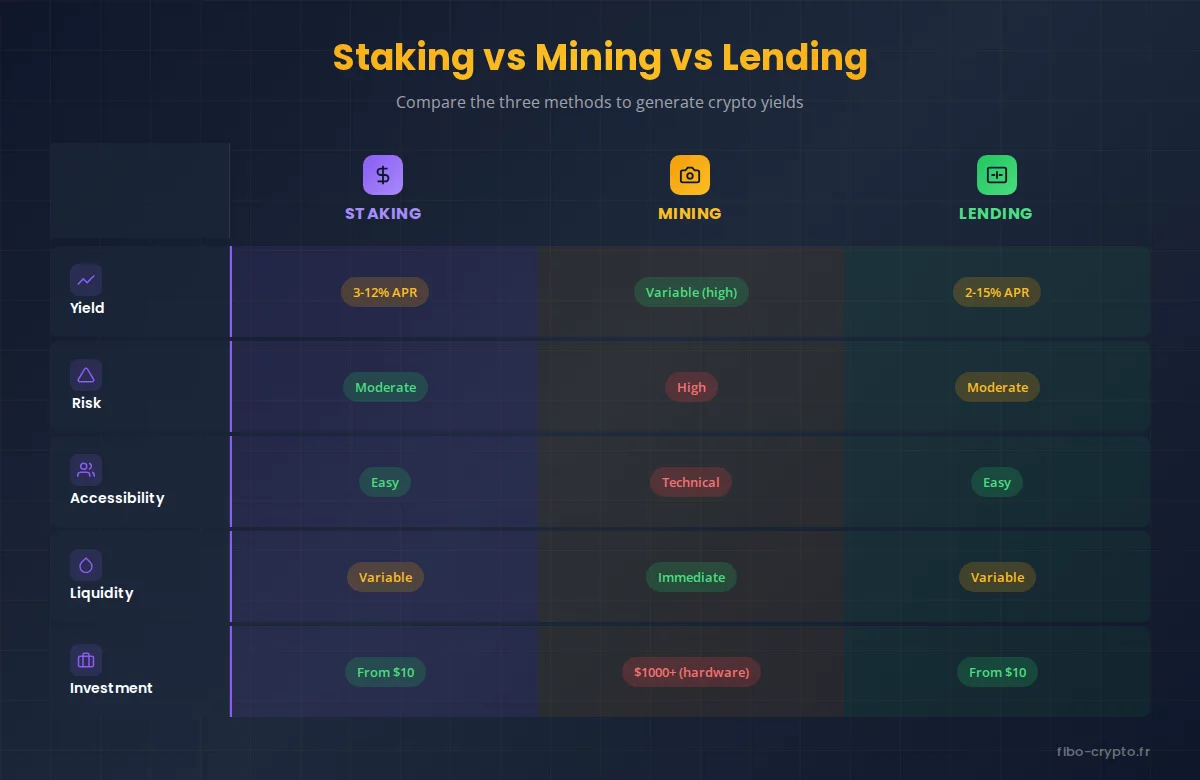
Staking vs Mining
Mining (Proof of Work) is still used by Bitcoin and a few other cryptocurrencies. It requires significant hardware investment (ASICs, GPUs) and cheap electricity to be profitable. Choose mining if: you have access to very cheap electricity and want to mine Bitcoin. Choose staking if: you want passive income without hardware investment or technical skills.
Staking vs Lending
Lending (cryptocurrency loans) allows you to generate interest by depositing your assets on DeFi protocols like Aave or Compound, where they will be lent to borrowers. Unlike staking which secures a blockchain, lending finances trading or investment activities.
Key differences:
- Mechanism: staking locks tokens to validate transactions; lending lends assets for interest
- Returns: staking 3-12% APR (stable); lending 2-15% APR (variable based on supply and demand)
- Risks: staking exposes you to slashing and lock-up; lending exposes you to smart contract bugs and liquidations
- Liquidity: lending generally offers more flexibility (withdraw anytime on DeFi protocols)
Choose lending if: you want potentially higher returns, keep your liquidity, or diversify your DeFi strategies. Choose staking if: you prefer contributing to a blockchain’s security and accept lock-up periods.
Both strategies are complementary: you can stake part of your ETH and lend your stablecoins on Aave to optimize your portfolio.
Practical Example: Paul’s Story
Nothing beats a practical example to understand staking. Let’s follow Paul, a beginner investor who decides to stake his first ETH. Paul owns 2 ETH that he bought at $2,000 each ($4,000 total). Not having the 32 ETH required for solo staking, he explores his options. Step 1: Choosing the method Paul hesitates between Lido (liquid staking) and Coinbase (exchange staking). He chooses Lido to:
- Maintain liquidity (receive tradeable stETH)
- Potentially use his stETH in DeFi later
- Avoid counterparty risk from a centralized exchange
Step 2: Staking via Lido Paul connects his MetaMask wallet to stake.lido.fi, stakes his 2 ETH, and receives 2 stETH in exchange. Lido fees: 10% of rewards. Step 3: The rewards With a 3.5% APR (after Lido fees):
- Year 1: 2 × 0.035 = 0.07 ETH in rewards
- Year 5 (with compound interest): ~2.38 ETH
Result: Without doing anything, Paul generated an additional 0.38 ETH in 5 years. If ETH rises to $5,000, his 2.38 ETH would be worth $11,900 (versus $10,000 if he had simply held his 2 ETH without staking).
The Future of Staking
Staking is set to become the industry standard with the increasing adoption of Proof of Stake and the emergence of new innovations like restaking.
Trends to Watch
- Restaking (EigenLayer): reuse your staked ETH to secure other protocols and multiply returns
- Liquid Restaking Tokens (LRTs): a new asset class combining liquid staking and restaking
- Staking ETFs: regulated financial products integrating staking for institutional investors
- Distributed Validator Technology (DVT): reducing solo staking risks by distributing responsibility among multiple operators
Regulation
The U.S. SEC has considered some staking services as securities, leading to lawsuits against Kraken and Coinbase. In Europe, the MiCA framework should provide more regulatory clarity by 2025.
📚 Glossary
- APR (Annual Percentage Rate): annual yield rate, without taking compound interest into account
- APY (Annual Percentage Yield): annual yield rate including compound interest
- Attestation: a validator’s vote confirming the validity of a proposed block
- Delegation: the action of entrusting your tokens to a validator without transferring ownership
- Epoch: a time period during which validators are assigned to their tasks (6.4 minutes on Ethereum)
- Liquid Staking: a method allowing you to stake while receiving a liquid token representing your position
- Lock-up: the period during which staked funds cannot be withdrawn
- Proof of Stake (PoS): a consensus mechanism where block validation depends on the amount of tokens staked
- Restaking: reusing already-staked tokens to secure additional protocols
- Slashing: a penalty applied to validators who violate protocol rules
- Validator: a network node responsible for verifying and proposing new blocks
- Unbonding period: the delay required to withdraw your tokens after initiating unstaking
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
Is staking profitable in 2025?
Yes, staking remains profitable with returns of 3 to 12% depending on the cryptocurrencies. However, actual profitability depends on the price movement of the staked token. A 5% APR doesn’t compensate for a 30% price drop.
What’s the minimum to start staking?
With liquid staking (Lido, Rocket Pool) or exchanges, you can start with just a few dollars. Solo staking on Ethereum requires 32 ETH (approximately $80,000).
Are my cryptos safe while staking?
With solo staking or non-custodial liquid staking, you retain control of your funds. On centralized exchanges, you’re exposed to platform bankruptcy risk.
How are staking rewards taxed?
Staking rewards are generally taxable upon receipt in most jurisdictions. The specific treatment varies by country—consult a tax professional familiar with cryptocurrency for your particular situation.
What’s the difference between APR and APY?
APR (Annual Percentage Rate) is the gross rate without reinvestment. APY (Annual Percentage Yield) includes compound interest. A 5% APR with monthly reinvestment yields approximately 5.12% APY.
Can I lose my crypto while staking?
Yes, through the slashing mechanism if your validator commits a serious fault. The risk is minimized with reputable validators. On exchanges, bankruptcy risk is also present.
How long does it take to withdraw staked funds?
This varies by protocol: immediate with liquid staking (selling stETH), several days to weeks for native staking (unbonding period). On Ethereum, expect 1 to 5 days depending on the network queue.
📚 Sources
- Ethereum Foundation – Official Proof-of-Stake documentation
- Lido Finance – Liquid staking protocol documentation
- Staking Rewards – Yield data and analytics
- Coinbase Learn – Beginner’s guide to staking
- EigenLayer – Restaking documentation
How to cite:
Fibo Crypto. (2026). Crypto Staking: Complete Guide to Generating Passive Income. Retrieved from https://fibo-crypto.fr/what-is-staking
